A Content Delivery Network is a set of servers located in different locations and networked via the Internet. It’s a great way to get your website or web app out to the world. By using such a network, your server connects to a multitude of other servers. Using a dispatch system, static content from your web server is transmitted to so-called mirror servers. When users load specific content from your website, this request is transmitted by a request routing system to the most suitable mirror server of the Content delivery network to deliver the corresponding data. The number and distribution of servers vary with the content network provider, as does the degree of integration and the performance of the Internet backbone.
Summary
- Here’s how CDN data is delivered
- Why choose a CDN
Here’s how CDN data is delivered
Users cannot know whether the data for a site comes directly from the outgoing server or from a mirror server, because this whole process takes place in the background. On the other hand, they may notice low loading times.
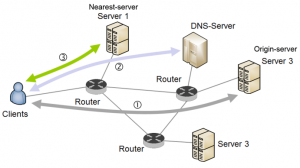
The two most important components in this process are the dispatch system and the Request-Routing System. The dispatch system not only transmits the contents of the origin server to the mirror servers, but it also takes care of their topicality and their veracity. Two procedures are possible for this: either the distribution system sends the modified and new data directly to all the servers of the Content Delivery Network, or it only sends a message informing that such data is on such a mirror server so as to make it available during user requests. To ensure that these user requests reach the right servers at the right time, the Request-Routing System is activated. The latter ensures that requests are redirected optimally, in two steps.
Finding the right mirror server
The first step is to find the most suitable server to meet user demand. To meet this objective, the request routing system is based on specific indicators, calculated with different measurement methods. We can determine with these different indicators whether they are connections from the Web client or from the server. It is possible, thanks to the measured values on the server side, which count the general load on the processors or the number of active accesses on the server, to determine which mirror server to use, which is the one with the lowest load. With regard to the properties of the connection between the client and the server, the Request-Routing-System determines the server with the best connection to the client. Key factors include latency, average transmission rate, packet loss rate, but also geographic proximity. Client-side indicators tell us about the identity of the user making the request. The system uses them, for example, if the content has to be delivered in different qualities for standard and premium customers.
Furthermore, the evaluation of the various indicators always depends on the data requested: the generation of dynamic content is rather carried out with a server having good indicators, while a stable connection between client and server represents the basics of use of streaming media.
Request Redirection
If the target server is known in the CDN, the next step is to redirect the request via the Request-Routing-System. There are several methods for such request redirection, which differ fundamentally according to the location of the redirection, between a mirror server, on the client or the network.
Redirection of the client’s request is a simple method to set up: the client chooses the mirror server from a list presented. However, it has the disadvantage that the Content Delivery Network has little influence on the allocation of servers. An http 302 redirect is also simple to implement and has good information on the CDN. In this case, the output server responds with the http status code when requested and informs the client of the appropriate mirror server, which will be contacted automatically for other requests. The main drawback of this process is the duplication of the necessary connections.
The most frequent way of redirection is Request-Routing based on the DNS (Domain Name System or system of domain names in French). The client’s request is transmitted to a special DNS server within the Content Delivery Network, which in turn returns the IP address of a mirror server. The biggest annoyance of this process is that repeated consultations in the DNS slow down access.
Why choose a CDN
With servers scattered around the world, your customers can benefit from faster load times and less exploitation of bandwidth capacity. As an operator, you also have considerable advantages in using a content delivery network. The load on your web server is not only lightened by redirecting requests, but the security of the data in the buffer memory is also increased. Thus, DDoS attacks cannot reach the outgoing server. Some prerequisites are however necessary for this. You should keep sensitive data such as user data or passwords away from the CDN, as this poses a higher risk of attack, regardless of whether it involves frequent conflicts in protection Data. Assigning content removed from a CDN to your own domain name helps prevent the spread of a potential cyber attack on another element of the website. The following list summarizes the benefits of a content delivery network:
- Static elements such as HTML pages, images, style sheets, documents or scripts on the client side are saved in the cache memory of the mirror server and no longer have to be loaded from their Web server afterwards. This saves the server, but also offers shorter loading times to your users. As a result, you will benefit from a reduced bounce rate and better SEO on search engines;
- The low usage of the server and the applications involved protects the server from overload, damage or possible failures. This has positive consequences on the material that we need for hosting;
- You can decide for yourself which static client elements you can load from the server to the Content Delivery Network. If you only upload images from your Blog, for example, they can be loaded in parallel, which will speed up loading times;
- Websites take advantage of this sending of data via CDN for streaming music and videos, because large amounts of data must be moved in a short time. This also applies to live broadcasts on Internal;
- Increases in the number of visitors or peaks of visits are easily controlled. The search for mirror servers with lighter loads by a Request-Routing-System proves to be very profitable, in particular if you offer files for download or if you operate an online store;
- You not only shorten the load times, but also reduce the bandwidth load, with which the content loads are linked,
- The security of your server and therefore of its data and of the applications used is increased with a Content Delivery network, because attacks are recognized in time and immediately diverted.
About the author
DMTwebhosting.com’s Editorial Team prides itself on bringing you the latest web hosting news and the best web hosting articles!
You could also link to the news and articles sections:
http://www.DMTwebhosting.com/blog